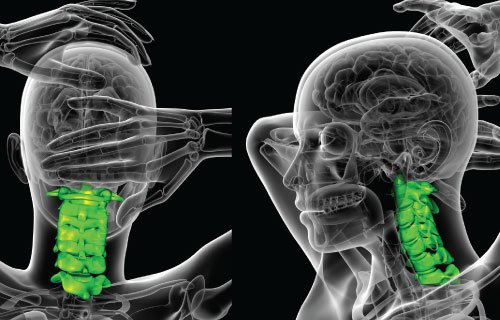
What Is Arthritis of the Back and Neck?
Arthritis of the back and neck is a condition characterized by inflammation and stiffness in the spinal joints, causing pain and reduced mobility. Common types include osteoarthritis and rheumatoid arthritis. Diagnosis involves medical assessments, and treatment may include medications, physical therapy, and, in severe cases, surgery. Managing symptoms is crucial for improving the overall quality of life for individuals affected by this condition.
Symptoms of Back and Neck Arthritis
Usually, symptoms begin gradually and worsen over time. After a prolonged period of sitting, or when you first wake up, pain and stiffness may be at their worst. Severe pain can also develop following intense activity.
- Loss of flexibility and stiffness: It could be difficult to straighten your back or turn your neck.
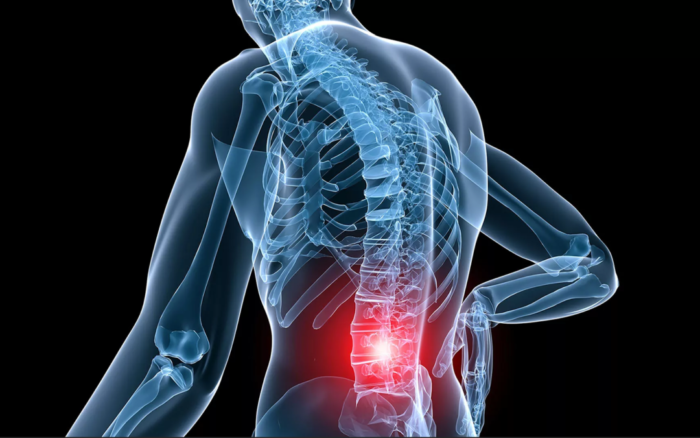
- Pain: The most common location of pain is in your lower back.
- Crepitus: When you move, you might experience a grinding sensation.
- Tenderness and swelling: You may feel soreness to the touch along the afflicted joints in your back.
Causes of Back and Neck Arthritis
There is no known cause of OA. The following are some typical variables that contribute to OA:
- Age: Your odds of developing OA increase with age.
- Weight: Obesity is associated with a higher risk of osteoarthritis.
- Stress: Repetitive joint strain from athletics or employment may raise your risk.
- Injury: OA may result from a back injury.
- Genetics: Some individuals have an OA family history.
Diagnosis of Back and Neck Arthritis
You and your doctor will have a physical examination to determine whether you have arthritis in your back. To check for damage to the joints in your spine, they will most likely order an X-ray. To rule out other illnesses, they might also prescribe blood tests.
Treatment of Back and Neck Arthritis
1. Medications:
- Pain Relievers: Prescription or over-the-counter drugs that reduce pain and inflammation, such as acetaminophen or nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).
- DMARDs, or disease-modifying antirheumatic medications: are prescribed to slow the progression of autoimmune arthritis types, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
2. Physical Therapy:
- Customized stretches and workouts that improve flexibility, build muscle and improve posture.
- Physical therapists use manual therapy techniques to help patients with pain and stiffness.
3. Frequent observation and follow-up:
- Regular assessments by medical specialists to determine the efficacy of treatment and make necessary modifications to the management plan.
- Concerns or changes in symptoms should be discussed openly.
For Better Consultation you can contact: Dr.Vivek Mahajan
Prevention of Back and Neck Arthritis
- Maintain a Healthy Weight
- Regular Exercise
- Practice Good Posture
- Quit Smoking
- Stress Management
- Hydration Matters

Thanks for sharing this amazing post! “Arthritis of the Back and Neck” is a valuable and accessible guide that empowers individuals with knowledge, aiding in informed decision-making and promoting collaboration between patients and healthcare providers. By addressing the full spectrum of this condition, the resource contributes to a better understanding of arthritis and its management within the context of spinal health.