What is a knee replacement surgery?
Knee replacement surgery, or total knee arthroplasty, is common for people with severe knee osteoarthritis. It involves replacing the damaged knee joint with an artificial joint made of metal and plastic. If you’re considering knee replacement surgery, it’s important to understand the procedure, what to expect, and the recovery process.
Different types of arthritis May affect the knee joints Osteoarthritis (Osteoarthritis) is a degenerative joint disease commonly found in middle-aged and elderly people. It can cause the joint cartilage and adjacent bones in the knee to break down. rheumatoid arthritis Pain is caused by inflammation of the synovial membrane and results in excess synovial fluid. Stiffness can also occur. traumatic arthritis Arthritis due to injury can cause damage to the knee cartilage.
The goal of knee replacement surgery is to restore damaged parts of the knee joint. And to relieve knee pain that cannot be controlled by other treatments.
Anatomy of the knee
A joint is an area where two or more bones meet. Most joints are mobile. Makes bones able to move Basically The knee is two long bones held together by muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Each end of the bone is covered with a layer of cartilage that absorbs shock and protects the knee.
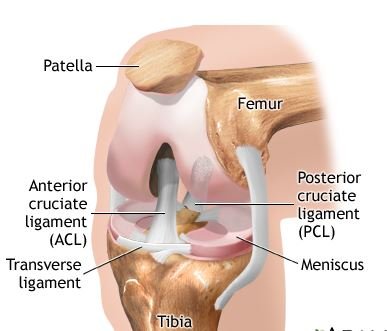
There are two groups of muscles in the knee: the quadriceps (located at the front of the thigh) which helps lengthen the leg; and the hamstring muscle (located at the back of the thigh), which flexes the knee of the leg.
Tendons are connective tissues that connect muscles to bones. Ligaments are elastic tissues that connect bone to bone. Certain knee ligaments provide stability and protection to the joint. while other ligaments It limit the forward and backward movement of the shin bone. (shin bone)
The knee consists of the following:
- Skin Bone: This is the shin bone or larger of the lower leg.
- Meniscus. A curved part of cartilage in the knees and other joints acts as a shock absorber, increases the contact area, and deepens the knee joint.
- Femur This is the thigh bone or upper leg bone.
- Synovial membrane. A tissue that lines the joint and seals it into a joint capsule. The synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid (a clear, sticky fluid) around the joint to lubricate it.
- Cartilage A type of tissue that covers the surface of bones in joints. Cartilage reduces friction from movement in the joint.
- Synovial membrane Tissue that lines the joint and seals it in the joint capsule. The synovial membrane secretes synovial fluid. (clear, viscous fluid) around joints to lubricate
- Muscle tendon A type of hard and flexible connective tissue that restricts joint movement to provide support around it.
- Tendon A type of tough connective tissue that connects muscles to bones and helps control joint movement.
- The meniscus is the curve of cartilage in a joint, such as the knee, that absorbs shock. increase contact area and make the knee joint deeper.
Knee Replacement Surgery Procedure:
- Pre-Operative Preparation: Before the surgery, you’ll undergo a series of tests, including blood tests, X-rays, and possibly an MRI. Your surgeon will discuss the procedure, risks, benefits, and alternatives. You may also be asked to stop taking certain medications and follow specific dietary guidelines.
- Anesthesia: The surgery is typically performed under general anesthesia, meaning you’ll be completely asleep during the procedure.
- Incision: The surgeon makes an incision on the front of your knee.
- Joint Removal: The damaged knee joint is removed, including the cartilage, bone, and meniscus.
- Implant Placement: The artificial joint, consisting of a metal femoral component, a plastic tibial component, and a plastic patella component, is implanted in place of the damaged joint. The components are secured using screws and cement.
- Closure: The incision is closed with stitches or staples.
At-Home Recovery and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy: When leaving the hospital Physical therapy is an important part of the recovery process. Dr. Mahajan will create a personalized rehabilitation plan for you. This may include:
- Exercises to strengthen the muscles in the knee area A variety of exercises to increase flexibility and avoid stiffness. Gradual resumption of daily activities with appropriate support
- Wound care: Keep the surgical area clean and dry. The great male doctor will give you specific instructions on how to care for your wound. Any signs of infection (redness, swelling, or fever) should be reported immediately.

- Follow-up appointments: To monitor your progress and ensure your knee implant is performing as expected, Dr. will have regular checks with Vivek Mahajan. X-rays may be taken to confirm proper implant placement.
Conclusion
Knee replacement surgery is a life-changing procedure that can relieve chronic pain and restore mobility. in orthopedic surgery and patient-centered care With Vivek Mahajan’s expertise, you are in trustworthy hands. His personalized approach ensures that every patient receives the highest level of care before surgery for a full recovery.